European scientists say they have made a major breakthrough in their quest to develop practical nuclear fusion – the energy process that powers the stars.
The UK-based JET laboratory has smashed its own world record for the amount of energy it can extract by squeezing together two forms of hydrogen.
If nuclear fusion can be successfully recreated on Earth it holds out the potential of virtually unlimited supplies of low-carbon, low-radiation energy.
The experiments produced 59 megajoules of energy over five seconds (11 megawatts of power).
This is more than double what was achieved in similar tests back in 1997.
It’s not a massive energy output – only enough to boil about 60 kettles’ worth of water. But the significance is that it validates design choices that have been made for an even bigger fusion reactor now being constructed in France.
“The JET experiments put us a step closer to fusion power,” said Dr Joe Milnes, the head of operations at the reactor lab. “We’ve demonstrated that we can create a mini star inside of our machine and hold it there for five seconds and get high performance, which really takes us into a new realm.”
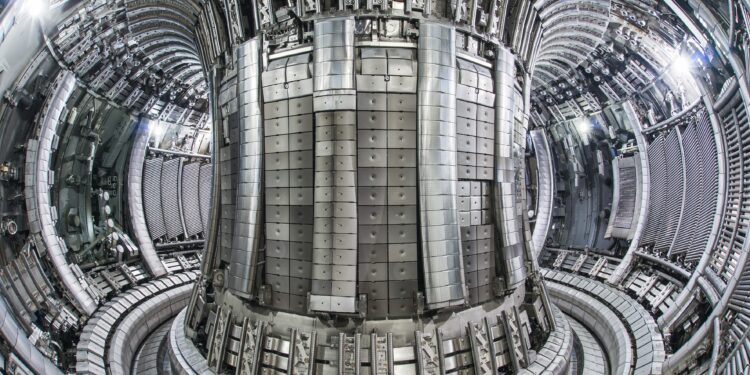
The ITER facility in southern France is supported by a consortium of world governments, including EU member states, the US, China and Russia. It is expected to be the last step in proving nuclear fusion can become a reliable energy provider in the second half of this century.
Operating the power plants of the future based on fusion would produce no greenhouse gases and only very small amounts of short-lived radioactive waste.
“These experiments we’ve just completed had to work,” said JET CEO Prof Ian Chapman. “If they hadn’t then we’d have real concerns about whether ITER could meet its goals.
“This was high stakes and the fact that we achieved what we did was down to the brilliance of people and their trust in the scientific endeavour,” he told BBC News.

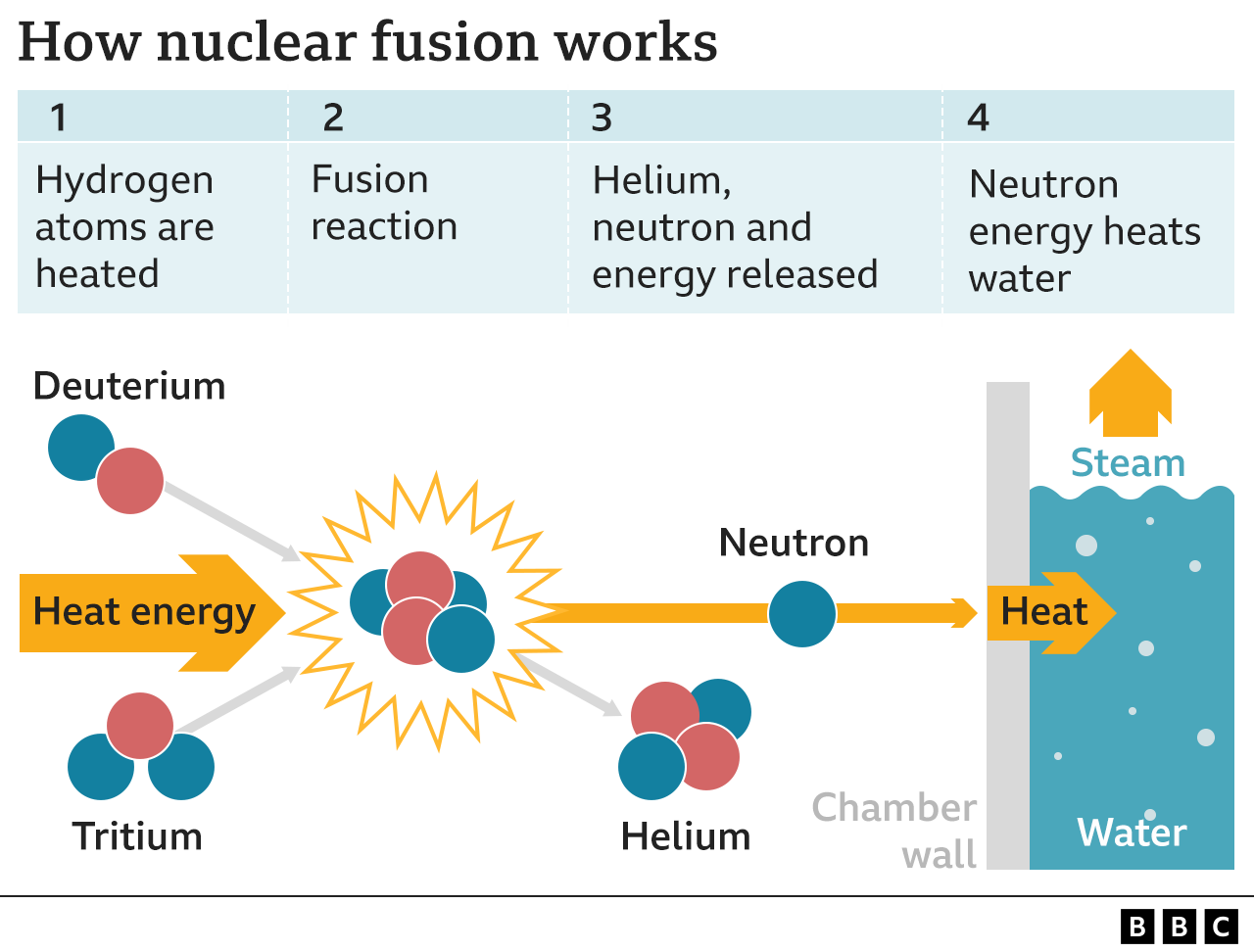
Fusion works on the principle that energy can be released by forcing together atomic nuclei rather than by splitting them, as in the case of the fission reactions that drive existing nuclear power stations.
In the core of the Sun, huge gravitational pressures allow this to happen at temperatures of around 10 million Celsius. At the much lower pressures that are possible on Earth, temperatures to produce fusion need to be much higher – above 100 million Celsius.
No materials exist that can withstand direct contact with such heat. So, to achieve fusion in a lab, scientists have devised a solution in which a super-heated gas, or plasma, is held inside a doughnut-shaped magnetic field.
The Joint European Torus (JET), sited at Culham in Oxfordshire, has been pioneering this fusion approach for nearly 40 years. And for the past 10 years, it has been configured to replicate the anticipated ITER set-up.
Source: BBC










Recent Comments