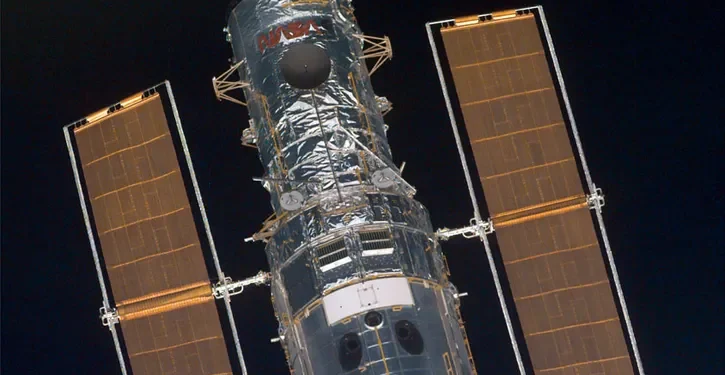
For over three decades, the Hubble Space Telescope has stood as an emblem of human curiosity, ingenuity, and perseverance in exploring the cosmos. Launched on April 24, 1990, aboard the space shuttle Discovery, this revolutionary observatory has reshaped our understanding of the universe, unveiling its mysteries with unprecedented clarity and depth.
One of Hubble’s most significant contributions has been its ability to peer deep into the cosmos, capturing images of distant galaxies, nebulae, and other celestial phenomena with unparalleled detail. By orbiting above Earth’s distorting atmosphere, Hubble delivers breathtaking views that have not only captivated the public but have also transformed our understanding of the universe’s vastness and complexity.
Moreover, Hubble has played a pivotal role in cosmological research, providing crucial data to support theories about the universe’s age, expansion rate, and composition. Its observations of distant supernovae led to the discovery of dark energy, a mysterious force driving the universe’s accelerating expansion—an achievement that earned three astronomers the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2011.
Beyond cosmology, Hubble has revolutionized our understanding of planetary science. Its keen eye has captured detailed images of planets within our solar system, revealing dynamic weather patterns, volcanic eruptions, and other phenomena. These observations have not only deepened our understanding of planetary processes but have also provided valuable insights for future space exploration missions.
Furthermore, Hubble has served as a vital tool for studying the birth and death of stars. Its observations of stellar nurseries—vast clouds of gas and dust where stars are born—have provided astronomers with valuable insights into the mechanisms driving star formation. Additionally, Hubble’s observations of aging stars shedding their outer layers have shed light on the process of stellar evolution, enriching our understanding of the life cycle of stars.
In its more than three decades of operation, Hubble has undergone several servicing missions, each extending its capabilities and lifespan. These missions, carried out by astronauts aboard the space shuttle, have replaced aging components, installed new instruments, and repaired technical glitches, ensuring that Hubble remains at the forefront of astronomical research.
As we celebrate the Hubble Space Telescope’s remarkable legacy on its anniversary, we also look forward to the future of space exploration. While Hubble continues to unlock the mysteries of the cosmos, its successor, the James Webb Space Telescope, stands poised to push the boundaries of discovery even further. Together, these observatories represent humanity’s insatiable curiosity and our relentless pursuit of knowledge about the universe we call home.
newshub


Recent Comments