His support looks weaker, but his grip on power has never been stronger
President Recep Tayyip Erdogan has been in power for more than 20 years and now faces his stiffest challenge yet.
Six opposition parties have combined forces for presidential and parliamentary elections on 14 May, picking opposition leader Kemal Kilicdaroglu as their unity candidate.
Turkey has become increasingly authoritarian under President Erdogan and the opposition is seeking to reverse that.
He appears vulnerable, with Turkey facing soaring inflation and reeling from twin earthquakes that have left more than 50,000 people dead.
Any candidate who can secure more than half the presidential vote on 14 May is the outright winner. Failing that, the race goes to a run-off two weeks later.
Erdogan’s election challenge
Turkey’s 64 million voters have been polarised for years, but Mr Erdogan, 69, is under pressure as never before as opinion polls suggest his main rival for the presidency has the edge.
His AK Party has been in power since November 2002, and he has ruled Turkey since 2003. A new generation of nearly five million first-time voters has never known any other leader.
Initially, he was prime minister but then became president in 2014, reacting to a failed 2016 coup by dramatically increasing his powers.
Now he runs the country from a vast palace with much of the media controlled by allies.
Increasing numbers of Turks have blamed him for soaring inflation, because of his unorthodox refusal to raise interest rates. The official inflation rate is just above 50%, but academics say it is actually higher than 100%.
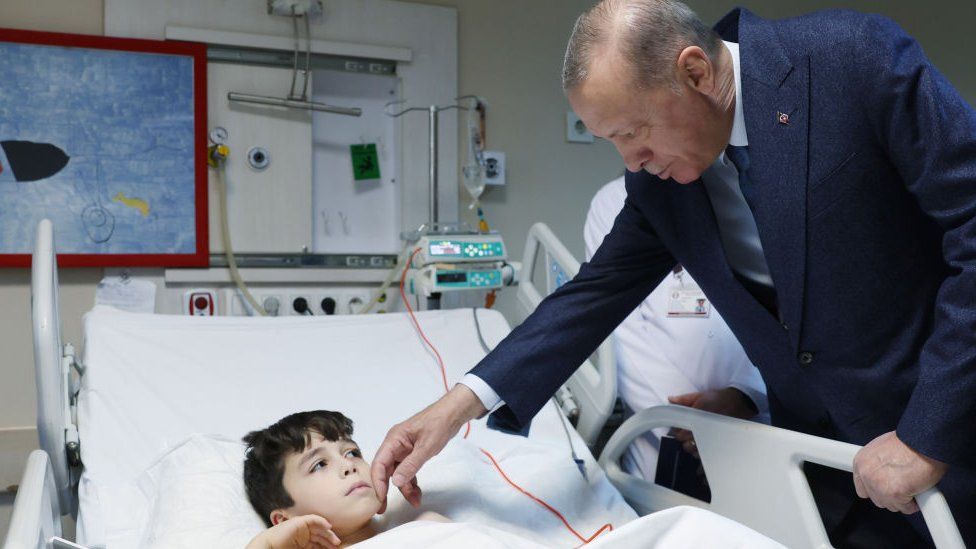
In the wake of Turkey’s catastrophic twin earthquakes on 6 February, he and his ruling party have been widely criticised for mishandling search and rescue efforts but also failing to adopt construction practices in earlier years.
Millions of Turks were left homeless in the 11 provinces affected by the quakes. Since many of the areas are seen as Erdogan party strongholds, the election could be won and lost in the east.
His AK Party is rooted in political Islam, but he has forged an alliance with the ultra-nationalist MHP.
Six opposition parties – one candidate
Kemal Kilicdaroglu, 74, comes across as a mild-mannered, bookish opponent and he has presided over a string of election defeats at the helm of the main opposition Republican People’s Party (CHP).
But this time could be different as he is fighting as a unity candidate for six opposition parties, ranging from his own centre-left party and the nationalist Good party to four smaller groups, which include two former Erdogan allies one of whom co-founded the AK Party.
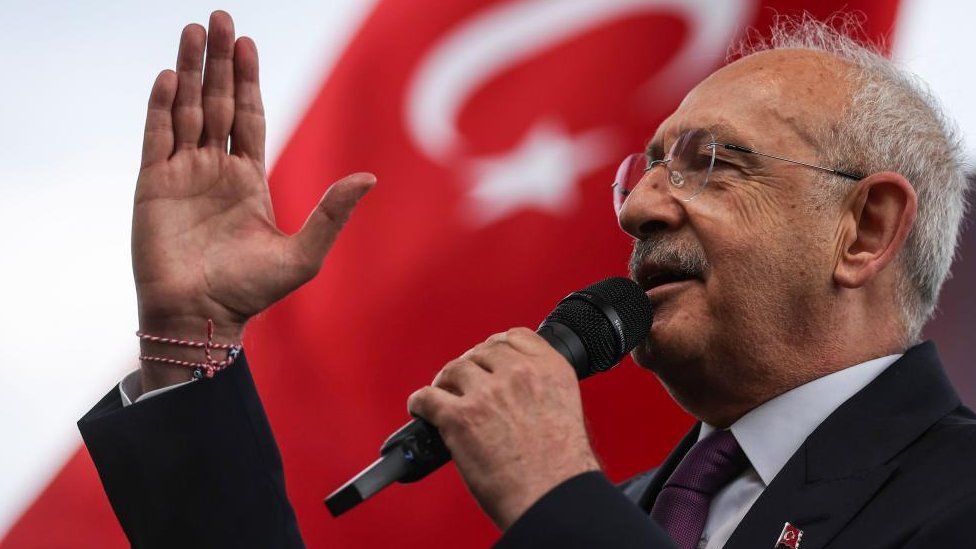

Significantly, Mr Kilicdaroglu also has the explicit backing of Turkey’s second-biggest opposition party, the pro-Kurdish HDP, whose co-leader has described the elections as “the most crucial in Turkey’s history”.
Because of a court case alleging links with Kurdish militants, the party is running for parliament under the banner of another party, the Green Left and is not fielding its own candidate for the presidency.
Kemal Kilicdaroglu’s selection was not universally popular as the mayors of Istanbul and Ankara were potentially stronger candidates. Both are party colleagues who took control of Turkey’s two biggest cities in 2019 for the CHP for the first time since 1994.
A former civil servant who is part of the Alevi minority, Mr Kilicdaroglu led a 24-day march for justice in 2017 which was seen as the biggest show of defiance against President Erdogan’s rule for years.
His Nation Alliance, also known as the Table of Six, are united in their desire to return Turkey from the presidential system created under Mr Erdogan to one led by parliament. To change the system, they need to win 400 of Turkey’s 600 MPs, or 360 MPs to take a proposal to a referendum.
The leaders of the other five members of the alliance have agreed to take on the roles of vice-president.
Dramatic withdrawal of candidate
There were four candidates in the race for the presidency, but with three days to go before the vote, a former centre-left party colleague of Mr Kilicdaroglu dropped out, blaming deepfake videos targeting him on social media.
Mr Ince, 58, ran for the presidency for the Republican People’s Party presidential candidate in 2018, but left two years later because of differences with Mr Kilicdaroglu.
His withdrawal could boost his former colleague’s chances, even though his poll ratings were low. Mr Ince had faced accusations of diluting the opposition vote, but pointedly, he has not urged supporters to back his former colleague.
The only other candidate still in the race is ultra-nationalist Sinan Ogan, but he has a limited chance of success.
How does the vote work?
To enter the 600-seat parliament, a party needs to attract 7% of the vote, or be part of an alliance that does.
That is why alliances have become so important in Turkey, and the six-party opposition have highlighted changing that as one of their proposed reforms.

Turks vote for party lists rather than candidates under proportional representation, so seat numbers correspond to votes cast per party rather than alliances.
The four smaller parties in the main opposition Nation Alliance will challenge for parliament under the banner of the two biggest parties: the CHP or the nationalist Good Party.
The ruling AK Party is party of the People’s Alliance, but its individual parties are fighting the election separately.
Candidates running for the Green Left instead of the pro-Kurdish party are part of the six-party Labour and Freedom Alliance. All but one of the six parties will run under the banner of the Green Left.
Under the Erdogan reforms, it is now the president who chooses the government, so there is no prime minister. And if his broad People’s Alliance fails to win a majority in parliament, he may struggle to rule in the same way as now. The pro-Erdogan People’s Alliance currently has 334 MPs.
Mr Erdogan has already served two terms as president, so a third appears to go against the rules of Turkey’s constitution.
But Turkey’s YSK election board ruled that his first term should be seen as starting not in 2014 but in 2018, when the new presidential system began with elections for parliament and president on the same day.
Opposition politicians had earlier asked the YSK to block his candidacy.
How would the opposition change Turkey?
The Kilicdaroglu-led Nation Alliance wants to restore Turkey’s parliamentary system and reform the presidency, removing the head of state’s right to veto legislation, cutting the post’s ties to political parties and making it electable every seven years.
The six parties also want to kickstart Turkey’s decades-long bid to join the European Union and restore “mutual trust” with the US, after years of fractious relations during the Erdogan years.
They have pledged to bring inflation below 10% within two years and send Syrian refugees home voluntarily. Turkey currently hosts some 3.6 million Syrian refugees.
Source: BBC











Recent Comments